Versioning¶
FleCSI’s versioning system uses three branch types (descibed below) that define the purpose and provenance of the code at a particular commit, with tags that label points of interest in the development cycle, e.g,. releases or stable features.
Branch Types¶
incompatible
The devel branch is where work on the next major release takes place, potentially with interface and feature changes that are incompatible with previous versions.feature
Feature branches (named for their major version number, e.g., 1, 2, 3) are for feature development on the current major version.release
Release branches (named for their major.minor version number, e.g., 1.1, 1.2) are stable versions of the code base. These can only be modified with bug fixes. At appropriate points, tags (named for their major.minor.patch version number, e.g., 1.1.2) are used to identify patched versions.
Tip
At the time of writing, FleCSI has the following branches:
devel (incompatible)
1 (feature)
1.4 (release)
Tags¶
The form of a tag is determined by the underlying branch type and commit it is intended to reference:
devel branch
In general, a commit on the devel branch should only be tagged if it is the first commit after a new feature branch has been created, and should be named with d and the major version of the feature branch, e.g., when feature branch 2 is created, a new devel tag d2 should be created on the next devel commit.feature branch
Feature tags should be created on the next commit after a new release branch is created, with f and the major.minor version of the release branch, e.g., when release branch 1.5 is created, a new feature tag f1.5 should be created on the next feature commit.release branch
Release tags should be created for each new release, with v and the release version, e.g., v1.4.1.
Tip
Tags mark a whence or origin for development rather than a whither or completion. The first letter of the tag is important, i.e., d, f, or v, as it is used by FleCSI to determine the branch type of the tag during CMake configuration.
Workflow¶
FleCSI development uses a devel -> feature -> release forking workflow that can be visualized as in Fig. 2. Bugfixes and features can be back-merged into feature or devel, as appropriate.
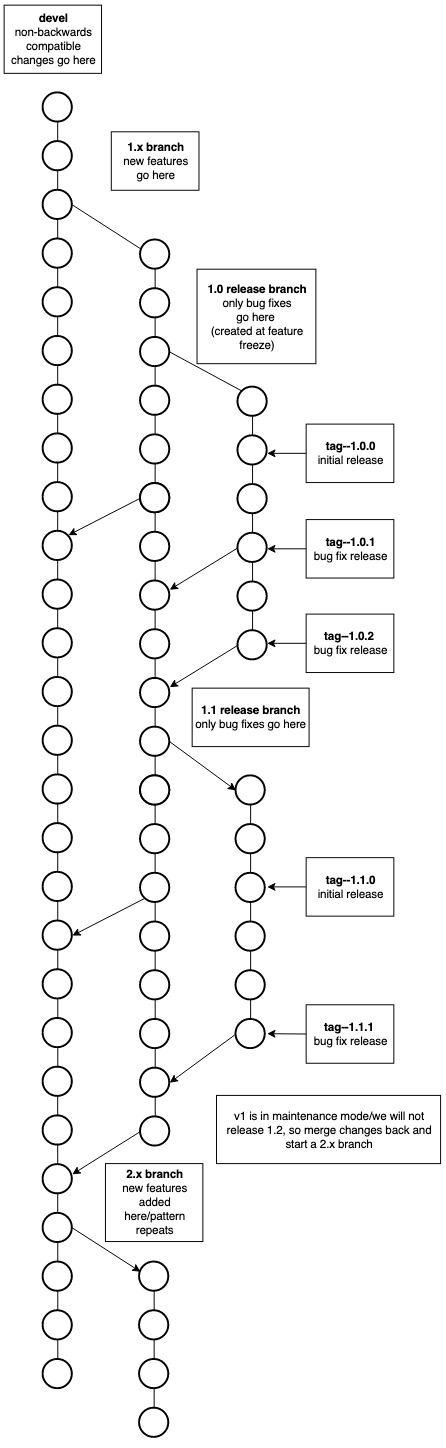
Fig. 2 Workflow diagram illustrating basic workflow using the three branch types described above. (Figure due to Angela Herring.)¶